Digital technologies for real-time health data and decision-making
UNDP’s approach
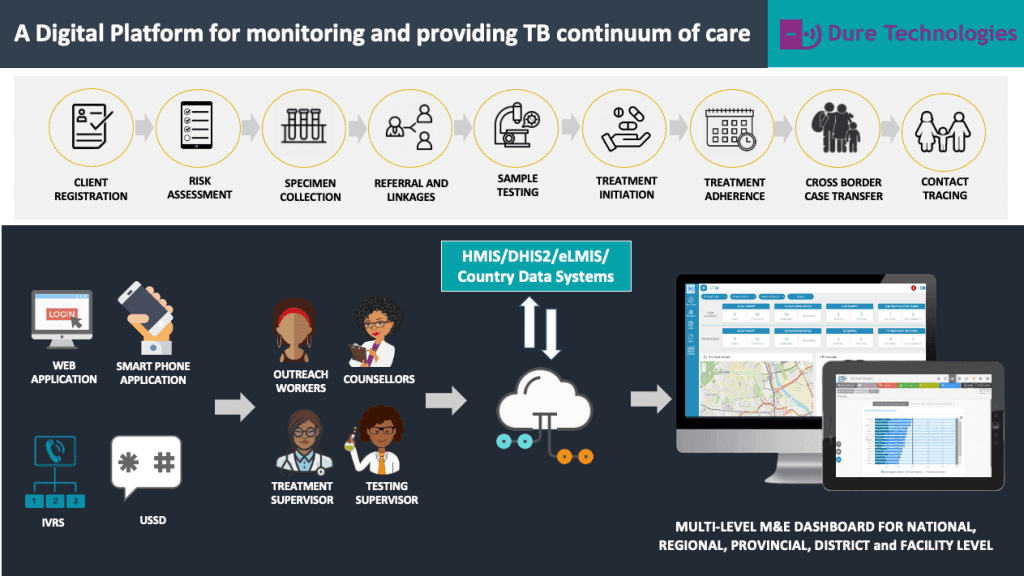
Among the applications of digital technologies that UNDP promotes in the health sector are those aimed at strengthening real-time capture, monitoring, and use of data within national HIV, malaria, tuberculosis and other health programmes. This support ranges from the digitalization of national health information systems, such as through the roll-out of the electronic district health information system (DHIS-2), and the use of mobile technologies within disease surveillance and tracking systems. UNDP likewise helps countries to identify and adapt open-source digital tools suitable for resource constrained contexts, including those to support disease monitoring, prevention, diagnosis, and recovery efforts in COVID-19 and beyond. This page provides some examples of digital health technologies that have supported countries to leverage data to enhance the coverage and quality of disease prevention and treatment efforts. Visit the Health information systems section for more information on UNDP’s broader capacity development support to strengthen health management information systems.
UNDP’s support to data systems and tools in the health sector is informed by its digital strategy to harness the potential of digital transformation for development, as well as guided by core Principles for Digital Development. It is important to ensure that amidst the heightened interest in the potential benefits of digital health, all people enjoy the benefits of innovation and that digital technologies help to reduce inequalities. To achieve this, UNDP is committed to ensuring that efforts in utilizing digital technologies are anchored in the values and obligations defined by the United Nations Charter and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.